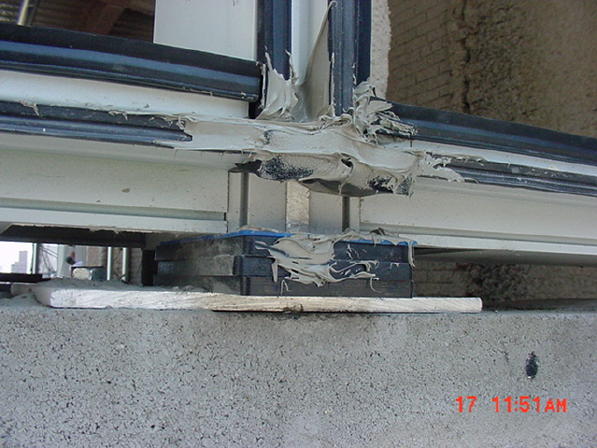
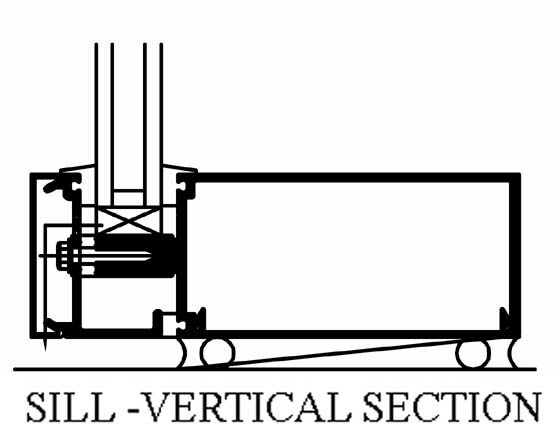
This photo shows the base of a curtain wall vertical mullion with the anchor standing on the CMU wall. Two horizontal mullions are connected at both sides of the vertical mullion. The mullion is supported on the plastic shims visible in front.
The picture below shows the typical detail of this condition, with the sealant joint adhering to the bottom surface of the horizontal mullion. Unfortunately, there is not enough surface for sealant adhesion: neither at the edge of the horizontal mullion nor at the edge of the vertical mullion. Most manufacturers require minimum ¼” width of substrate.
Also, any attempts to caulk the gap between the vertical mullion and the top of the CMU wall are futile because the plastic shims break this joint.
The additional challenge comes from the existence of differential movement joints between the ends of the horizontal mullions and the sides of the vertical mullion. They are designed to let the shrinkage and expansion of horizontal mullion caused by temperature differentials.
This joint should be continuous around the curtain wall perimeter. Unfortunately, there are no horizontal mullions at the corners; therefore, gaps are created. Also, the joints accommodating the structural deflections (e.g. story drift at jambs and vertical differential movement at heads) would require to be sized accordingly. The 100% elastic sealant joint would need to be 1-3/8”wide to accommodate the typical combination of a ½” differential movement and a 3/8” combined tolerance.
This detail is extremely vulnerable to the human factor and it may not last long even if carefully designed and produced.
The architect shall specify the curtain wall, with bolts connecting the bottom anchor and the vertical mullion, as opposed to utilizing shims for support. The architect shall also draw the details of a curtain wall in such a manner that a reasonable room at the perimeter conditions is provided to allow proper support, waterproofing, tightness, acoustical and thermal barrier, consider the tolerances (i.e. differences between story heights) and in case of fire rating partitions: fire and smoke barrier.